On this page
Sign up to our newsletter
Subscribe to receive the latest blog posts to your inbox every week.
By subscribing you agree to with our Privacy Policy.
What is this guide and how to use it?
An overview of how KODE OS evolves current building operations from a reactive to a predictive approach. KODE OS suite of applications utilize advanced machine learning algorithms to capture issues before they arise. Thereby optimizing equipment by adjusting their runtime and increasing their lifespan.
Introduction
Proactive maintenance represents a strategic shift in commercial real estate, focusing on foresight and data-driven decisions to enhance maintenance and efficiency. KODE OS propels this shift by providing a platform that anticipates and informs operational strategies through advanced analytics. This proactive methodology extends equipment life, elevates tenant experiences, and optimizes building management.
Three advanced solutions power Proactive Maintenance
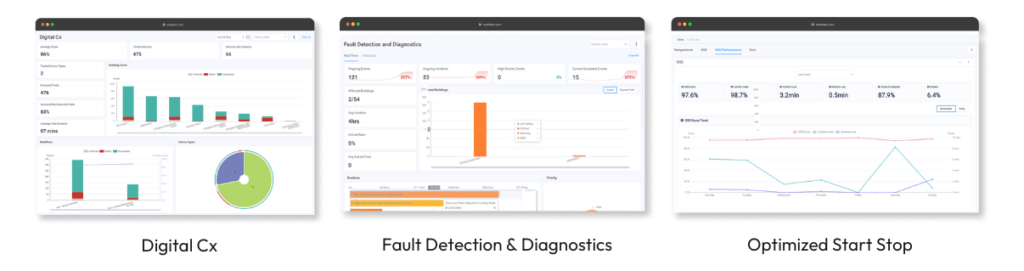
Proactive Maintenance in three steps

Step 1: Test your equipment with Digital Cx
Digital commissioning (DCX) enables real-time visibility into the health of your building(s). Commissioning can now be continuous, examining as many critical assets as is deemed necessary or building performance benefits. DCX is flexible with the number of equipment tested, how often and when. Predictive operations comes from being proactive, not reactive.

Step 2: Run FDD in the background to detect faults in advance
Identify the root cause of the fault happening based on a set of rules established around the operation of the equipment & continuous analysis.

Step 3: Run OSS to optimize your equipment running time and future proof your building operations
OSS uses machine learning to determine how to turn on and off the systems without sacrificing comfort. Typically used to test HVAC in commercial buildings, OSS optimizes the AHU start at a time that is sufficient to reach the desired setpoint in all of the connected VAVs.
Proactive Maintenance
How do you find issues before tenant complaints? How do you find them between annual maintenance checks? How do you get more efficient? How do you reduce the downtime of these issues?
That’s where Digital Cx comes into play and makes sure that your path to the future is faster.

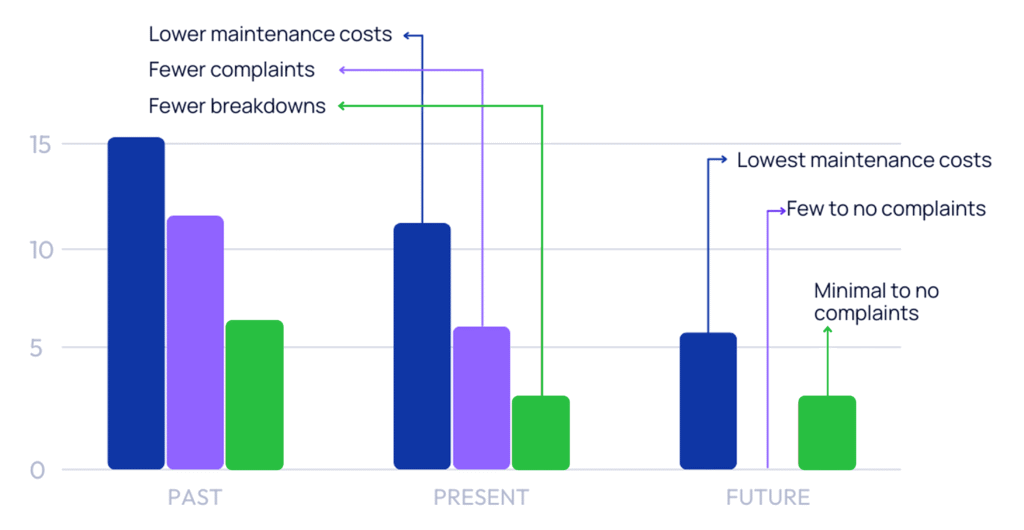
- Reactive maintenance based on equipment failure;
- Scheduled maintenance per manufacturer & regulatory guidelines;
- Paper-based maintenance log books;
- Operator intuition.

- Reactive maintenance on equipment failure (fewer);
- Preventative maintenance schedules based on historical data & best practices (more effective);
- Digitized maintenance log books & work order tracking;
- Informed decision making.

- Reactive maintenance on equipment failure (fewest / none);
- Proactive maintenance based on real-time data (most effective);
- Automated work order generation & tracking
- Actionable intelligence & data-driven decision making.
Proactive Maintenance with Digital CX
KODE OS leverages its Digital Commissioning (Digital Cx) capabilities to redefine maintenance operations, transitioning from rigid, calendar-based schedules to a fluid, data-driven approach. By continuously monitoring system performance and utilizing predictive maintenance strategies, KODE OS identifies potential issues before they escalate. This allows building operators to proactively address maintenance tasks, rather than adhering to a predetermined timetable.
For instance, instead of changing a filter every three weeks as a standard practice, KODE OS can optimize the operation such that the change is needed only after three and a half weeks. By evaluating the actual condition of equipment and considering factors like usage, air quality, and other environmental data, maintenance is aligned with utilization and scheduled accordingly.
This not only prolongs the life of the equipment by preventing over-maintenance but also aligns with the actual needs of the building’s operations, potentially leading to cost savings and more efficient use of resources. Digital Cx ensures that each action is precisely timed and necessary, enhancing the overall performance and reliability of the building systems.
Economic Impact on Maintenance Costs and Lease Rates
The adoption of predictive maintenance has significant financial benefits. By predicting and preventing issues, property managers can noticeably reduce costs associated with common area maintenance (CAM), thereby boosting net operating income by trimming operational expenses. Tenants enjoy stable and potentially lower lease rates resulting in an enhanced property market appeal. KODE OS integration and optimization tools play a pivotal role in achieving these cost reductions, ensuring real estate properties can maximize profitability and secure a competitive advantage.
Below, we’re taking a sample commercial building (Building A) with 400,000 square footage, $100,000 CAM annual expenses, and 25 different systems integrated with KODE OS. Taking the average annual operational savings we have observed since 2020 across hundreds of buildings using KODE OS and a sample $100/sf rent, the study highlights the impact of operational saving on both tenant lease rates and NOI for clients.
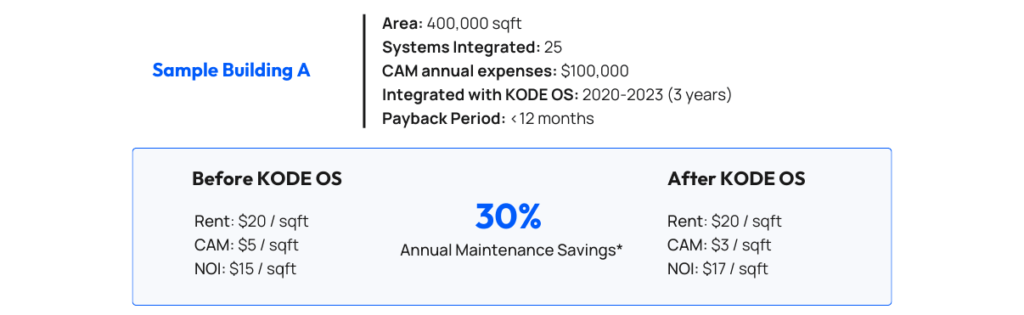
*Annual maintenance savings are observed and calculated across a combined portfolio of KODE notable clients (with 100+ buildings of commercial, retail, residential and mixed-use of different sizes, ranging from 100,000 sqft and above). All strategies as described, are actively running in these buildings.
Case Study
Operational excellence at Customer with two facilities*
Utilizing KODE OS, client was able to achieve substantial operational improvements across two of its’ facilities in only four weeks. KODE OS detected, prioritized and addressed inefficiencies that has projected annual savings of $0.18/sqft.
Via deployment of the KODE OS platform, multiple discrepancies and issues were surfaced with regards to the HVAC Controls present within the two sites. These issues can be categorized into three groups:
Configurational/Operation Issues
Identify the misconfiguration/mis-programming of HVAC equipment, which leads to suboptimal performance of the system.

Missing Data/Devices/Anomalous Sensors
Surface anomalous readings or data point properties that imply sensor issues or the lack of proper data points. These can reduce operational visibility into system performance.

Performance Issues
Visualize certain suboptimal behavior noticed within a space, even though the root cause may be unknown.
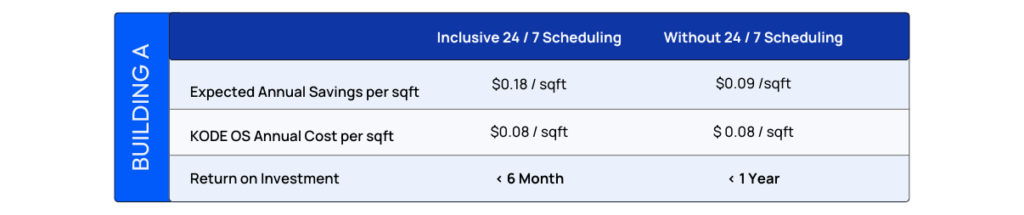
*Customer A – Building A, encompassing 95,000 square feet, and Building B, at 196,900 square feet, are referenced in our case study. This client has requested anonymity due to the sensitivity of data shared with third parties. For more detailed information, please contact your dedicated point of contact at KODE Labs.
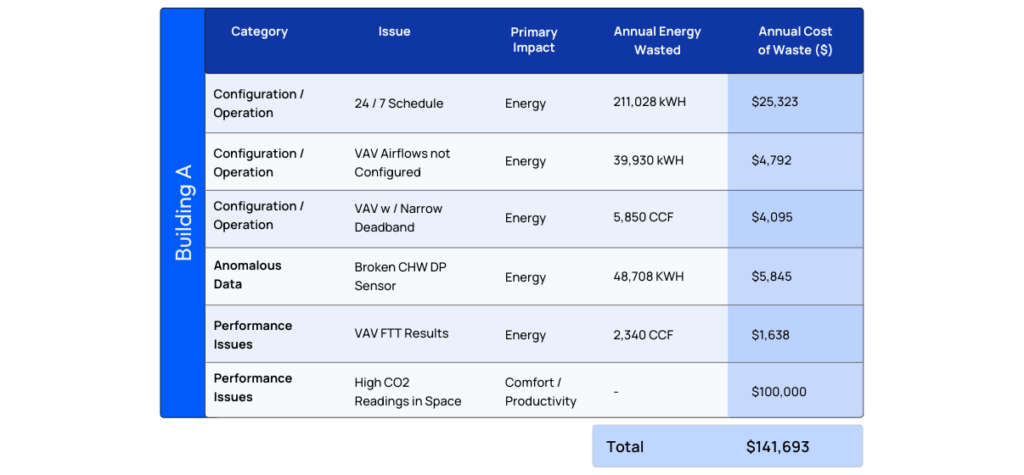
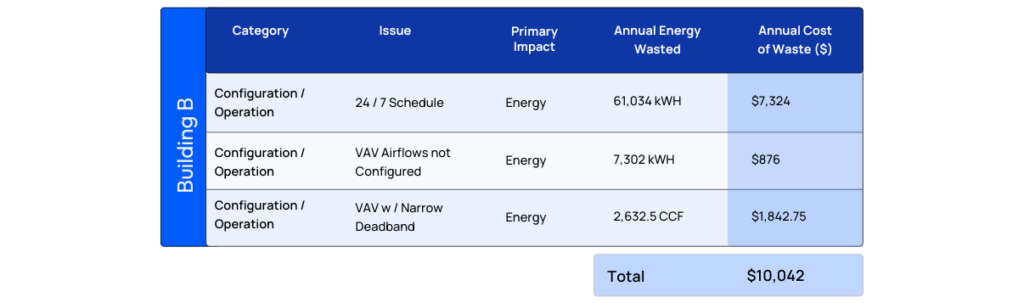
A number issues observed had a direct impact on energy consumption, while others impacted comfort/productivity of building occupants. The accompanying table aggregates all potential issues and showcases all KWH/$ savings.
KODE OS: Centralizing & standardizing technology
KODE OS is vendor agnostic and unifies any existing BAS systems, eliminating the need for multiple control points. This integration simplifies operations and reduces the clutter of redundant hardware. KODE OS’s insight into system performance allows facility managers to cut down on unnecessary equipment, lowering operational costs.
KODE OS identifies efficiency gaps, predicts maintenance issues, and cuts down on energy use. This proactive approach minimizes maintenance costs, directly reducing CAM fees and making property management more profitable.
Streamlining all technology with KODE OS
- 130+ API integrations: Connect to various data sources and systems, ensuring that your building operates harmoniously and efficiently.
- Independent Data Layer (IDL): Centralize your data management to facilitate real-time decision-making and analysis.
Smart building management
- Built-in analytics & reporting: Access actionable insights and comprehensive reports to make informed decisions and optimize operations.
- Energy management & optimization: Leverage energy optimization strategies to reduce energy consumption and operating costs in line with ASHRAE G36 principles.
- Remote command & control: Monitor and manage your building systems remotely, allowing for quick responses to changing conditions.
- Mass schedule management: Simplify the management of building schedules and occupancy requirements.
- Workflow Automation: Automate routine tasks and processes, freeing up time for strategic initiatives.
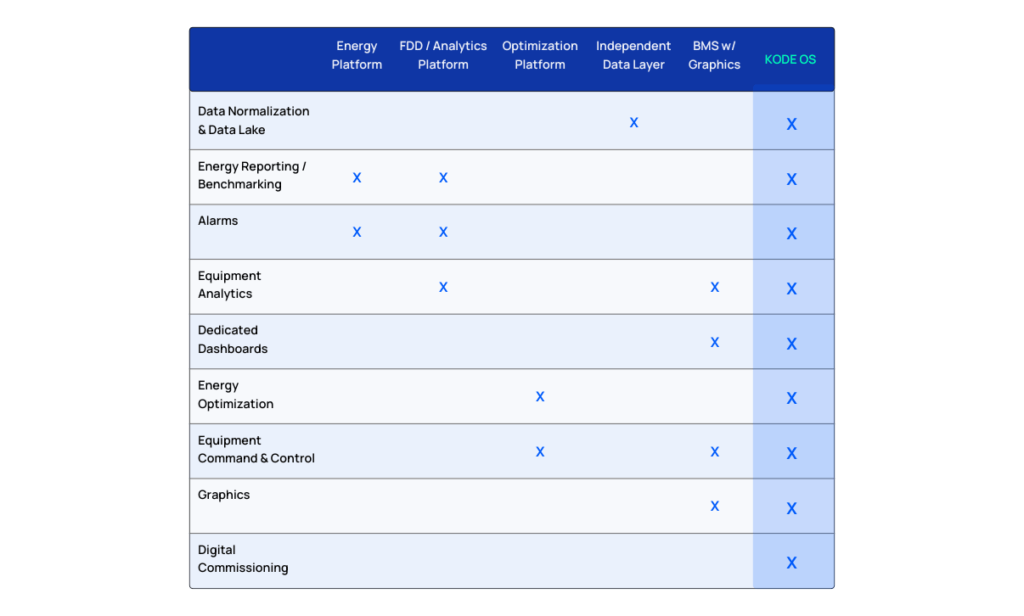
KODE OS: All in one platform
The features deployed and presented on KODE OS combine value propositions across multiple technology offerings along with providing unique features not available across any solutions today. KODE OS combines these features into a single-pane-of-glass interface, allowing requirements to be met for multiple teams, ranging from building operators to business decision makers. Below is a matrix that maps out how the different features deployed at the two sites overlap with other smart building/building technology solutions:
Additional Benefits
Automating Work Orders with KODE OS
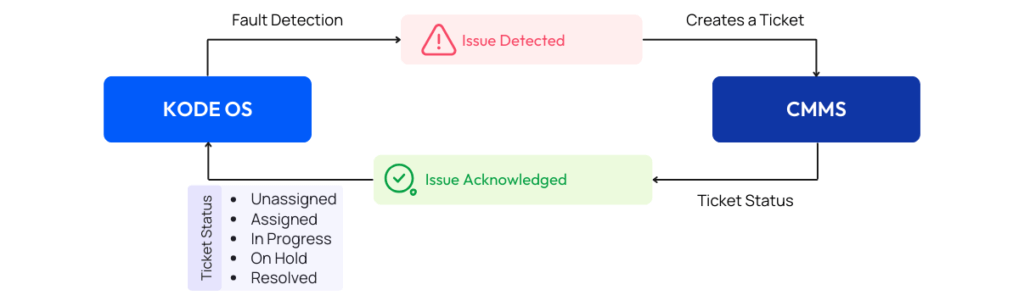
Scaling Asset Management with KODE OS presents an opportunity to transcend the limitations encountered with siloed Work Order Systems. While those solutions are good on their own, they often present hurdles such as high costs and complexity in deployment and scaling. In contrast, KODE OS is engineered to simplify and streamline work order generation right from Events Dashboard in KODE OS.

Work Order integration lets you configure Workflows that the Building Operations team wants to receive as a Work Order in their CMMS system. Users can dynamically configure how the Work Order is created based on the triggered Alarm. This ensures a seamless and fast assignment to the responsible building team to resolve the issue as quickly as possible.

Device operation and tenant satisfaction are crucial to building operators, so we offer an easy way to monitor device status and any type of defect as part of your everyday job from several different systems.

For any event that hasn’t been configured to be pushed to a Work Order system, users will have the ability to create and send the Work Order on-demand using the Event Data.
Integrating Metering and Utility Data
KODE OS automates utility billing data collection from multiple sources. KODE OS has API integrations developed with Energy Star Portfolio Manager for North American based buildings. This is utilized for clients who are actively using PM for benchmarking and tracking. The data pulled is based on the client’s inputs. KODE can provide support on how to set up, manage and utilize the free resource.
Supported Integrations
Urjanet – KODE OS has developed an API using Urjanet as a global solution to automate the utility bill data collection and data scraping process. This guarantees timely, up-to-date data for our clients with properties worldwide.
XLS Data – KODE OS is able to ingest utility bill data in a templated spreadsheet. The utility bill data will be input into a structured XLS file and uploaded into KODE Labs platform. If clients are already using a service for utility bill data and the platform has an API, we can develop an integration to the platform to collect and centralize the data into KODE OS. This includes major services such as CASS Utility Information Systems, Yardi, etc.

Optimizing Energy Usage
KODE OS normalizes energy and water metrics based on area, usage, and climate, enabling peer building comparisons. It also benchmarks against industry standards like Portfolio Manager, CBECs, and local thresholds like NYC’s Local Law-97, focusing on CO2e/sq ft.